
|
RWA 3-Grid Ecosystem — Architecture, Terminology and Functional Requirements** Draft International Standard (DIS) v0.9 Proposed by: Dadam Electronics Co., Ltd. (Republic of Korea) (World-first proposer of the 3-Grid Model for RWA Infrastructure) Foreword The rise of Real-World Asset (RWA) tokenization is establishing a new global paradigm for value exchange across finance, manufacturing, trade, digital identity, and sovereign data systems. Current RWA markets lack unified architecture for verification, legal enforceability, cross-border interoperability, and lifecycle integrity. The “RWA 3-Grid Ecosystem Standard” introduces a harmonized, multi-layered structure designed to ensure authenticity, trust, modular scalability, and international interoperability. This Draft International Standard has been proposed by Dadam Electronics Co., Ltd., based in the Republic of Korea, as the first structured RWA grid architecture intended for global adoption. Introduction RWA tokenization depends on the integrity of both physical assets and their digital representations. However, global markets operate without:
three-layer grid architecture (Grid 1–3) that ensures interoperability, verifiability, and regulatory alignment. 1 Scope This document specifies the architecture, terminology, functional requirements, and interoperability specifications for the global RWA 3-Grid Ecosystem Standard. It defines:
ISO 20022 — Financial Services Messaging ISO/IEC 27001 — Information Security Management ISO/IEC 20243 — Supply Chain Security ISO 17442 — Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) W3C DID Core Specification NIST SP 800-63 — Digital Identity Guidelines 3 Terms and Definitions 3.1 Real-World Asset (RWA) A physical or legally recognized asset whose properties are verified and digitally represented. 3.2 Digital Twin A verifiable digital representation of a real-world asset, linked through authentication procedures. 3.3 Grid 1 — Contractual & Smart Legal Layer The layer enabling legally enforceable digital agreements and rights. 3.4 Grid 2 — Physical-Digital Authentication Layer (PADT-RWA) Layer ensuring 1:1 asset–data binding, fraud prevention, and multi-factor verification. 3.5 Grid 3 — Modular Infrastructure Layer (RWA-MODULE) Layer enabling infrastructure deployment, lifecycle management, and multi-industry integration. 4 Symbols and Abbreviated Terms RWA — Real-World Asset PADT — Physical Asset Digital Twin DT-Auth — Digital Twin Authentication CBDC — Central Bank Digital Currency LEI — Legal Entity Identifier 5 System Overview The RWA ecosystem must guarantee:
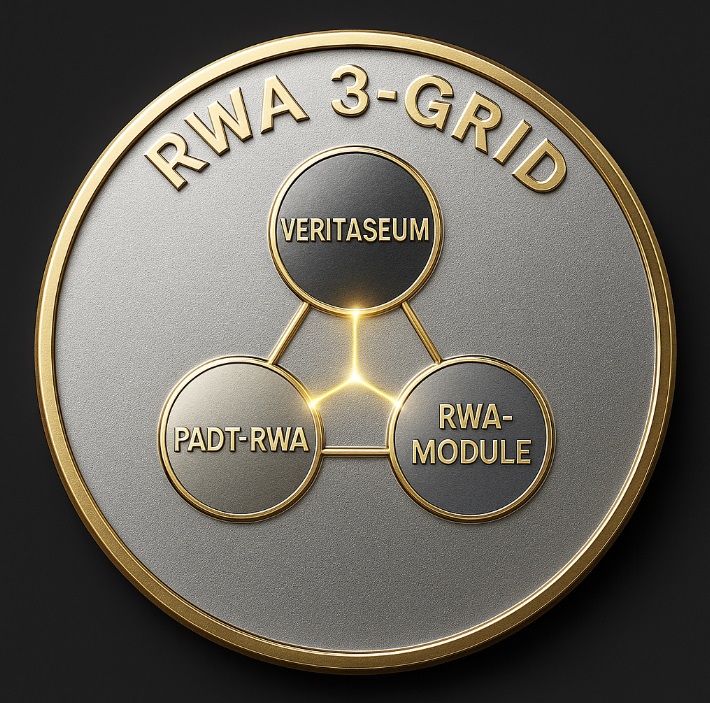
Grid 1 → Legal trust Grid 2 → Authenticity trust Grid 3 → Operational trust These three trust layers operate cohesively to form a unified global RWA standard. 6 Architecture of the RWA 3-Grid Ecosystem 6.1 Grid 1 — Veritaseum Layer (Smart Legal Agreements) Ensures:
Provides:
Includes:
The ecosystem must:
To be compliant with the RWA 3-Grid Standard, systems MUST:
Grid interaction diagrams (3-Grid triangular model) Annex B: Example Implementation CBDC–RWA integrated settlement model Annex C: National Certification Framework Example “K-Certification for RWA Authentication” |
🛡 Disclaimer
본 페이지 및 도메인들은
교육·연구·표준 안내 목적으로 제공되며,
특정 기업 또는 정부기관의 공식 정책을 대변하지 않습니다.
#Blockchain #Distributed #Ledger #Tokenization #Verification #Registry #Protocol #Layer
#P
ADT#PhysicalAsset#DigitalTwin #RWA #RWAtokenization #RealWorldAssets #AssetTokenization #DigitalTwin